What is XACML?
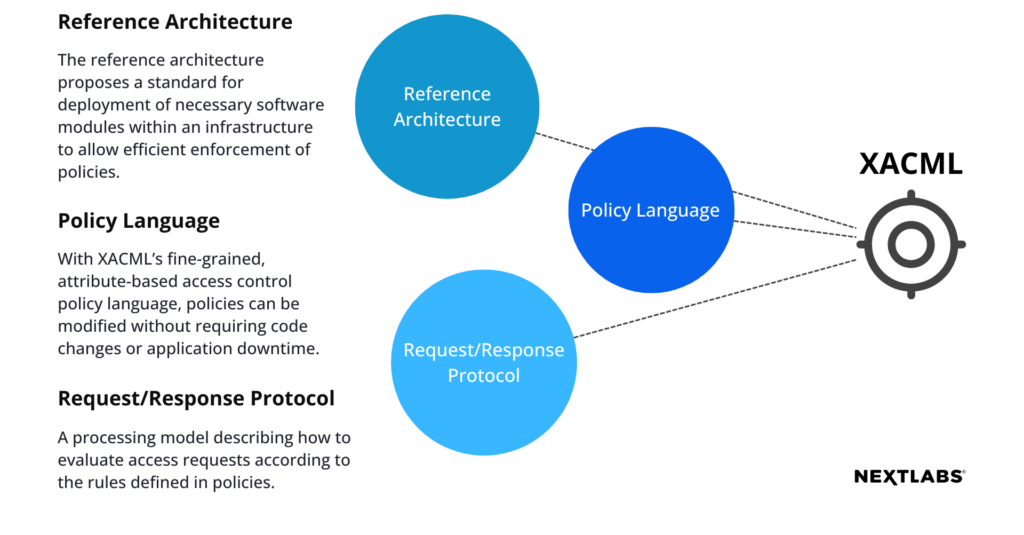
XACML is an OASIS Open standard. XACML stands for “eXtensible Access Control Markup Language”. It is an XML-based markup language designed specifically for Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC). The standard defines a declarative fine-grained, attribute-based access control policy language, an architecture, and a processing model describing how to evaluate access requests according to the rules defined in policies. The request/response language expresses queries about whether a particular access should be allowed (requests) and describes answers to those queries(responses). The reference architecture proposes a standard for deployment of necessary software modules within an infrastructure to allow efficient enforcement of policies.
According to Oasis Open, the typical use case is that someone wants to take some action on a resource. They will make a request to whatever actually protects that resource (like a filesystem or a web server), also referred to as a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP). The PEP will form a request based on the requester’s attributes, the resource in question, the action, and other information pertaining to the request. Next, the PEP will send this request to a Policy Decision Point (PDP), which will look at the request and the policy that applies to the request, and come up with an answer about whether access should be granted. Then, that answer is returned to the PEP, which can then allow or deny access to the requester. PEP and PDP may both be contained within a single application, or might be distributed across several servers. Besides providing request/response and policy languages, the XACML system also provides the other pieces of this relationship, like finding a policy that applies to a given request and evaluating the request against that policy to come up with a yes or no answer.
Why XACML?
There are several existing proprietary and application-specific languages for performing this action, but XACML has several points in its favor:
- XACML is standard. By using a standard language, you’re using something that has been vetted by a community of experts and users, therefore, you don’t need to roll your own system each time, and you don’t need to think about all the tricky issues involved in designing a new language. As XACML becomes more popular, it will be easier to implement with other applications using the same standard language.
- It’s generic. Rather than trying to provide access control for a particular environment or a specific kind of resource, it can be used in any environment. One policy can be written and applied within several distinct kinds of applications. When one common language is used, policy management becomes much easier.
- It’s distributed. This means that a policy can be written that refers to other policies kept in arbitrary locations. The result is that different people or groups can manage sub-pieces of policies as appropriate, as opposed to having to manage a single monolithic policy. XACML knows how to correctly combine the results from these different policies into one decision.
- It’s powerful. While there are several ways the base language can be altered and extended, many environments will not need to do so. The standard language supports a wide variety of data types, functions, and rules about combining the results of different policies. In addition, there are standards groups working on extensions and profiles that will hook XACML policy into other standards like SAML and LDAP, which will increase the number of ways that XACML can be used.
How Does XACML Affect Enterprises?
One main function of the XACML framework is to enable the development of effective security policies across the enterprise, instead of implementing individual policies for each point of access. The goal is to promote a common language and interoperability between access control implementations by multiple vendors.
As web access management has greatly evolved, several enterprises have embraced single sign-on systems with the separation of web-based authentication and coarse-grained authorization logic from applications. Despite this, when it comes to how organizations manage fine-grained authorization policies, significant challenges persist. To overcome these challenges, organizations must look beyond authentication and coarse-grained authorization towards a model of externalizing application authorization decisions. The XACML system is a mature standard framework built specifically for this.
Historically, RBAC has been the primary access control method used in enterprises, but it is no longer sufficient due to the explosion of access points and data volume. RBAC is limited to defining access permissions by role. This means it applies a sort of “one-size fits-all” solution which can be dangerous because it often results in too much or not enough access. Because users can be assigned multiple roles, it is possible that they contain conflicting data. This allows for loopholes in the permissions. RBAC also requires that administrators be extremely attentive to changes of users and roles and ensure that role assignment combinations are current, accurate, and consistent with other roles a user might be assigned.
ABAC, on the other hand, allows an enterprise to extend existing roles using attributes and policies. By adding context, authorization decisions can be made based not only on a user’s role, but also by taking into account who or what that user is related to, what that user needs access to, where that user needs access from, when that user needs access, and how that user is accessing the requested information. By creating a policy that is easy to understand, with context around a user and what s/he should have access to, access control becomes far more robust. This functionality expands the scope of RBAC significantly.
Enterprises have made significant investments in many business-critical applications and IT systems, however most of these applications and IT systems are based in RBAC. Therefore, enterprises are looking for ways to preserve their investment and extend the lifespan of these applications. ABAC and XACML offer an excellent option. XACML can be used as the standard to implement ABAC to extend RBAC or a hybrid ABAC and RBAC model.
Further, many enterprises have been developing custom solutions to meet the complex access control requirements of their business. However, this is a costly undertaking and it is difficult to maintain quality service. XACML can help enterprises break away from this dilemma by adopting a XACML-based commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) solution to eliminate the need to build a custom solution. With XACML’s fine-grained, attribute-based access control policy language, policies can be modified without requiring code changes or application downtime. This enables organizations to react quickly to changes in business or regulatory environments, greatly increasing agility and flexibility, and enhancing overall data protection while greatly reducing cost. Because access policies become centralized, altering the policies does not require software changes to individual applications. This results in a consistent enforcement of policies across key business applications – without relying on individual system administrators.
For a deeper dive into ABAC, read our Definitive Guide to Attribute-Based Access Control.
To comment on this post
Login to NextLabs Community
NextLabs seeks to provide helpful resources and easy to digest information on data-centric security related topics. To discuss and share insights on this resource with peers in the data security field, join the NextLabs community.
Don't have a NextLabs ID? Create an account.